There are a variety of techniques, methods, and tools that organizations, companies, and colleges use to block content on the Internet. In this article, we will discuss them in detail, as well as the various ways in which you can circumvent them. But before going any further, there are some basic technical Internet-related terms that we must discuss so that the rest of the article is easy and straightforward to understand.
IP address:
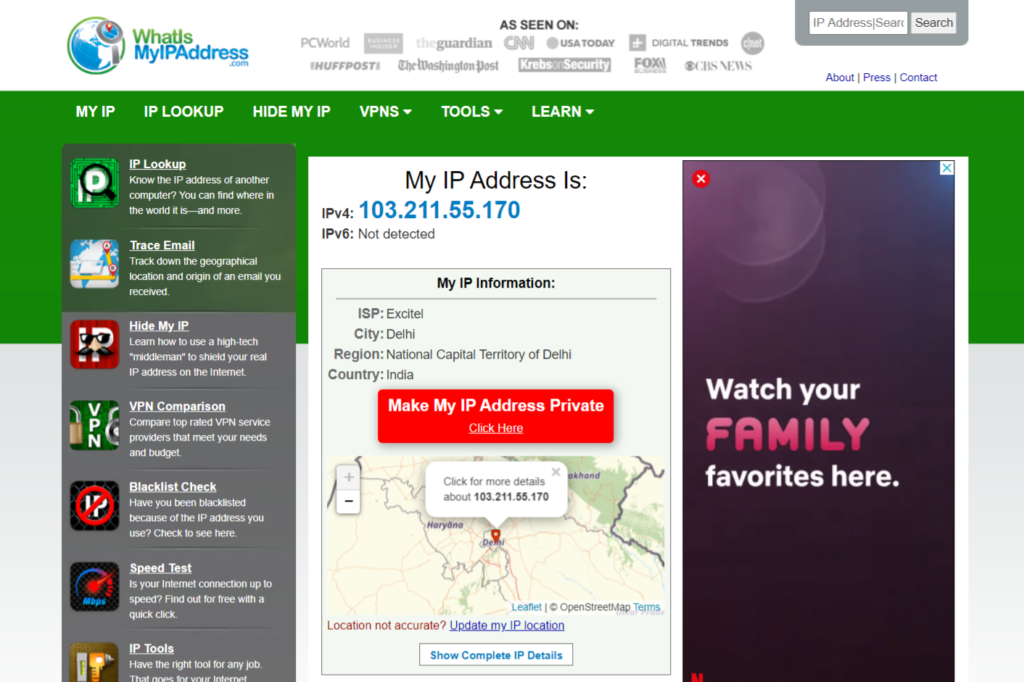
Every computer connected to the Internet has a unique IP address given to it. An IP address is a computer’s identity on the Internet at which it can be contacted. Without knowing somebody else’s IP address, you cannot communicate on the Internet with that computer or server. Your computer has an IP address. Your friend’s computer has an IP address, and even all your favorite websites on the Internet have their IP addresses. A typical IP address looks like the following: 203.14.11.12. You can find out your personal computer’s current IP address by only starting your browser and connecting to the website https://www.whatismyipaddress.com.
You can find out a website’s IP address (let us assume google.com) by merely going to MS-DOS for command-line prompt (click on the Windows Start Orb button on the left bottom corner of the screen and type CMD in the quick search bar) and type the command ping google.com. Within a few seconds in the output, the IP address of google.com will be displayed. In this case, it happens to be 216.58.196.68.

Domain name:
It is quite difficult to remember IP addresses since they are just a bunch of numbers. Imagine what a nightmare it would be if you had to remember and type an IP address in your browser each time you wanted to connect to any of your favorite websites. To make life simple for users, every website not only has an IP address but also has a corresponding domain name. A domain name is an easy-to-remember name for a website. For www.facebook.com is an example of a domain name, Unlike websites, usually, home computers do not have a domain name.
Domain name system (DNS) lookups:
The process of converting a domain name into its respective IP address is known as a DNS lookup. Your browser performs a DNS lookup automatically in the background each time you type a website address (or domain) in your browser. Without a DNS lookup, a browser will not know the IP address of the website you wish to connect to and hence will not know how to connect to it.
Reverse DNS lookup:
It is the exact opposite process of converting an IP address into its respective domain name.
DNS server:
A DNS server is a server that handles DNS lookup queries from browsers/users and sends back replies to them. Typically, your college, company, or organization will have its DNS server that will manage the local user’s DNS lookup requests.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol):
It is the communication protocol that is generally used by your browser to communicate with websites. It contains all the rules that browsers follow to interact with a remote website. The secure form of HTTP, which allows users to have encrypted communication with a website, is known as HTTPS.
Port:
A port is a door through which data enters or leaves your computer. Typically ports are used to exchange data between different devices. There are two types of ports:
- Hardware ports: All of us use hardware ports like USB ports, parallel ports, Ethernet port. These are generally used to exchange data between two devices.
- Virtual ports: All Web applications on your computer open something known as virtual ports on your computer communicate with remote servers on the Internet. Without virtual ports, there would be no way for applications on your computer to communicate with remote servers on the Internet. You can find a list of open virtual ports on your computer by only going to the MS-DOS prompt and typing the command netstat-n.
Proxy server:
A proxy server is a server or software that acts as an intermediary between a user and the Internet. Whenever a user sends a request for a webpage to a proxy server, the proxy server will forward that request to the relevant server on the Internet and then send back the response to the user. The working of a proxy server can be explained as given below:
- USER – sends a request for a webpage – PROXY
- PROXY – sends the same request to a relevant website – WEBSITE
- WEBSITE – sends back requested page – PROXY
- PROXY – sends back request page – USER
Based on the above schematic, it is evident that a proxy server can be used to protect one’s identity on the Internet. Usually, your computer will directly send a request to a website, and the website will know your computer’s identity or IP address. However, if you use a proxy server to send the request to a website, then the website will think that the proxy server is connecting to it. Still, the reality is you who is using a proxy server to connect the website anonymously.
Moreover, a proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user and the Internet. And it can be used to block access to some websites and prevent a user from connecting to them. A lot of governments, companies, and colleges use a proxy server along with a list of banned websites to restrict access to some websites.
On the other hand, some proxy servers do or block access to any website on the Internet. There are so many users, instead of connecting to the proxy server of their office or college, will connect to a proxy server that does not block anything to gain uncensored access to the entire Internet.
Although there are different types of proxy servers available on the Internet, the most popular types are the following:
- Web proxy or HTTP proxy: It is a type of proxy server that is primarily used to connect users with websites on the Internet using the HTTP protocol. Usually, a web proxy server will accept the requested web address in an input box within the browser window.
- DNS proxy: It is a type of proxy server that takes the DNS queries from the browser on a local network and forwards them to the nearest DNS server.
- SOCKS proxy: It is a type of proxy server that allows users to connect to a remote server using all different protocols like TCP, UDP, FTP, etc. Its use is not just restricted to giving users access to websites.
Different techniques are used by governments, companies, and colleges to censor the Internet and block access to websites and content on the Internet:
Domain name filtering:
Whenever you type a domain name in your browser, a DNS lookup query is sent to the local DNS server. It may be possible for a college or company to block DNS lookups for some domain names. If a browser cannot perform a DNS lookup for a particular domain, then it cannot access it. For example, if a network blocks DNS lookups for the Gmail server and the Google Talk server, then you will not be able to use your browser to connect to Gmail, nor will you be able to use your Google Talk Instant Messenger application since it will not be able to connect to the Google Talk server.
IP address filtering:
In such a filtering technique, instead of blocking domain names at the DNS server level, access to specific IP addresses are blocked by the network administrator.
Proxy filtering:
A lot of organizations will make all users connect to the Internet via a proxy server. The proxy server will monitor all the websites that users are trying to access and can be configured to block or redirect a user in case they try to access a website that the organization chooses to block
URL filtering:
In such a filtering technique, the entire URL address is scanned for certain blocked domains or keywords. In case any blocked domain or keyword is found, then the user is blocked and denied access to the respective website.
Port blocking:
To function correctly, some web applications open specific predefined local ports on your machine or establish outgoing connections to specific predefined ports on the remote computer. Without this, the applications cannot function and communicate on the Internet. To block the use of some applications, many network administrators will block the respective ports it uses to function. Such a technique effectively prevents the use of those individual applications. For example, to block the use of apps like Torrents and Skype, port blocking is commonly used.
Advance packet filtering:
In such a filtering technique, the transmission between a user and a remote website is monitored for specific keywords, and as soon as any blocked keywords are detected, then the connection is reset or disconnected.
Limits:
Some organizations like to limit the amount of data a particular user can download in a predefined period. As soon as that limit is reached, then the user’s access to the Internet is taken away. Instead of a data limit, some organizations also put a time limit on the Internet access of a user.
Complete disconnection:
This is usually seen only in case of emergency or unusual situations when a government disconnects users from the Internet entirely by removing the link between the users and the Internet.
Filtered access:
Many governments and organizations will allow users to search for only certain keywords on Google or access only specific videos on YouTube. This filter access is also a commonly used blocking mechanism.
